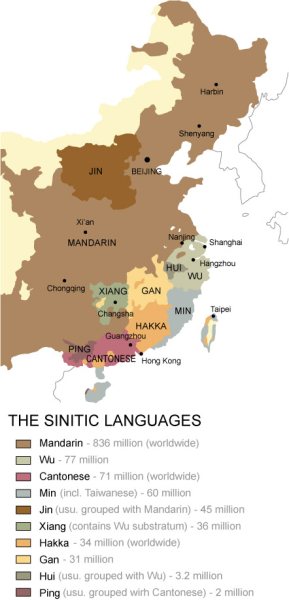
The
eight main dialect areas of Mandarin in Mainland

Jinan dialect
(simplified Chinese: 济南话; traditional Chinese: 濟南話; pinyin: jǐnánhuà) is a dialect of the Mandarin language family, which in turn constitutes one of the Sinitic language families. It is spoken in Jinan in Shandong province.
|
Consonants of the Ji nan dialect |
|||||||
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Tone chart of the |
|||
|
Tone number |
Description |
||
|
1 |
yin ping (陰平) |
˨˩˧ (213) |
dipping |
|
2 |
yang ping (陽平) |
˦˨ (42) |
falling |
|
3 |
shang sheng (上聲) |
˥ (55) |
high |
|
4 |
qu sheng (去聲) |
˨˩ (21) |
low |